| .. | ||
| models | ||
| src/main | ||
| cross_encoder_en_sdk.iml | ||
| pom.xml | ||
| README_CN.md | ||
| README_EN.md | ||
Download the model and put it in the models directory
Semantic Search - Re-Rank SDK [English]
For complex search tasks, using the Retrieve & Re-Rank pipeline can significantly improve search accuracy.
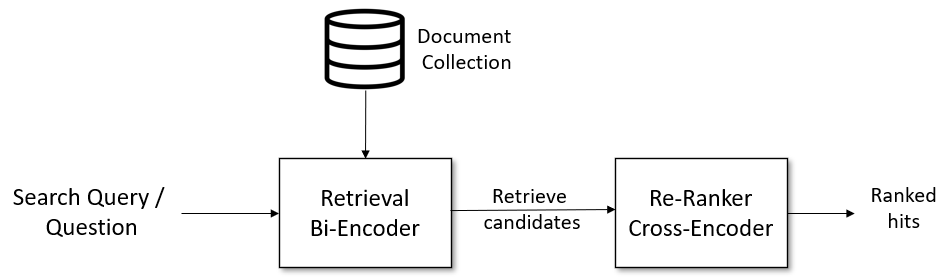
Retrieve & Re-Rank Pipeline
Typical pipeline for information retrieval / question and answer retrieval: Given a query statement, we first use a retrieval system to get a relatively large return list, such as: 100 relevant data. The retrieval system can use ElasticSearch or a vector search engine (extracting features through bi-encoder), such as faiss. However, the results returned by the search system may not be too relevant to the query statement (for example, the search engine does not consider performance and sacrifices some accuracy). At this time, we can use a re-ranker based on cross-encoder to re-sort the returned results in the second stage. Then present the reordered results to the end user.
Retrieval: Bi-Encoder
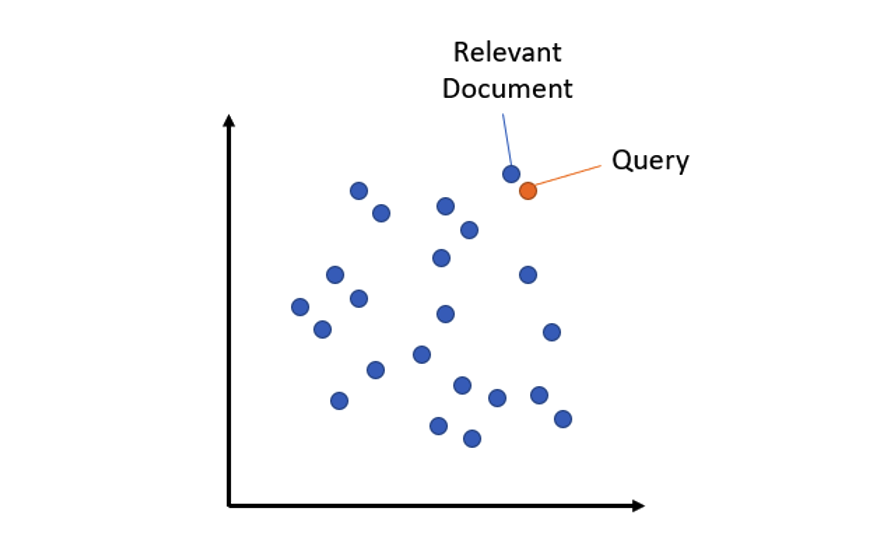
Semantic search retrieves the text in the corpus that best matches the query through sentence vector similarity. The model is trained based on the MS MARCO dataset and can be used for semantic search, such as: keywords / search phrases / questions. The model can find passages related to the query query. MS MARCO is a dataset composed of questions and answers released by Microsoft. Researchers in the field of artificial intelligence can use it to build question and answer systems that can rival humans. The full name of this dataset is Microsoft MAchine Reading COmprehension, which means "Microsoft Machine Reading Comprehension". MS MARCO is currently the most useful dataset of its kind because it is based on anonymous processed real-world data (search query data from Bing search engine).
The Bi-Encoder can use the following model:
https://github.com/mymagicpower/AIAS/tree/main/nlp_sdks/qa_retrieval_msmarco_s_sdk
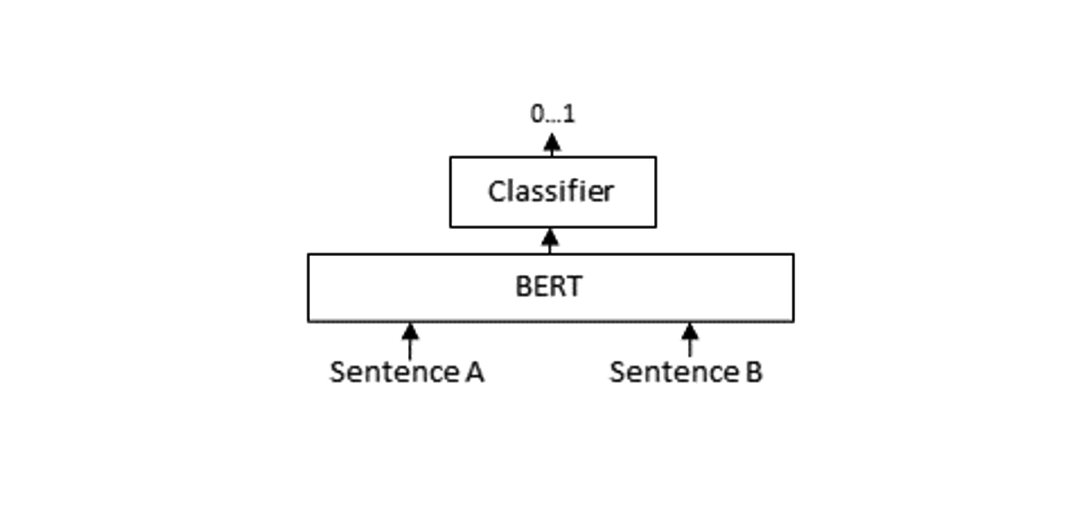
Re-Ranker: Cross-Encoder
Search engines are very efficient in retrieving a large number of documents, but they may return irrelevant candidates. At this time, the introduction of a re-ranker based on Cross-Encoder can further optimize the returned results. It passes the query statement and the previously obtained candidate items through a network at the same time to obtain a relevance score, and then sorts by this score.
SDK functions:
- Similarity calculation (max_seq_length 512)
Run the example-TinyBertCrossEncoderExample
After successful operation, the command line should see the following information:
...
...
# Test QA statement:
[INFO ] - input query1: [How many people live in Berlin?, Berlin had a population of 3,520,031 registered inhabitants in an area of 891.82 square kilometers.]
[INFO ] - input query2: [How many people live in Berlin?, Berlin is well known for its museums.]
# Calculate similarity score:
[INFO ] - Score1: 7.1523676
[INFO ] - Score2: -6.2870417
Open source algorithm
1. Open source algorithms used by the SDK
2. How to export the model?
-
Exporting CPU models (PyTorch models are special, and CPU and GPU models are not interchangeable. Therefore, CPU and GPU models need to be exported separately)
-
device='cpu'
-
device='gpu'
-
export_cross_encoder.py
from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSequenceClassification
import torch
from export import cross_encoder_wrapper
model = cross_encoder_wrapper.load_model('cross-encoder/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-2-v2')
# model = AutoModelForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('cross-encoder/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-2-v2')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('cross-encoder/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-2-v2')
txt_tok = tokenizer(['How many people live in Berlin?'], ['Berlin is well known for its museums.'], padding=True, truncation=True, return_tensors="pt")
print(type(txt_tok))
input_ids = txt_tok['input_ids']
print(type(input_ids))
print(input_ids.shape)
token_type_ids = txt_tok['token_type_ids']
input_mask = txt_tok['attention_mask']
input_features = {'input_ids': input_ids, 'token_type_ids': token_type_ids, 'attention_mask': input_mask}
model.eval()
#.logits
scores = model(input_features)
print(scores)
# strict=False
# Use torch.jit.trace to generate a torch.jit.ScriptModule via tracing.
traced_script_module = torch.jit.trace(model, input_features)
traced_script_module.save("models/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-2-v2/ms-marco-TinyBERT-L-2-v2.pt")